Industry 4.0 & artificial intelligence: 8 manufacturing applications for AI
Last updated on September 22nd, 2023
If you made a list of the most overused buzzwords in manufacturing today, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and Industry 4.0 (i4.0) would be right at the top of the list.
Runners-up would include the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), smart factories, and cyber-physical systems, with an honorable mention for blockchain. But these tarems are more than just buzzwords. Understanding the concepts behind them is crucial to staying competitive in modern manufacturing.
AI manufacturing buzzwords defined
You’ve probably heard some of these terms before and know that they are important when it comes to manufacturing in Industry 4.0. Let’s take a closer look at some of these buzzwords and how they relate to manufacturing data systems:
- Artificial intelligence is not about robots and androids. AI refers to human-like reasoning in computational systems. These systems are intelligent and they are able to solve problems much like a human brain would, but at a considerably greater speed and with a far higher level of accuracy. For example, using real time manufacturing analytics software, AI can classify items based on a certain set of features in a dataset.
- Machine learning is a type of artificial intelligence. It uses algorithms or statistical models to perform a task without being given explicit instructions. For example, machine learning can be used to differentiate between defective and good parts coming off an assembly line, without being supervised (unsupervised machine learning).
- Unsupervised machine learning is an algorithm that can group data points and features without instructions on what to look for. The model can map the underlying structure of a dataset, even without a specific target to predict. For example, in predictive quality software, machine learning can identify anomalies in production data that result from subtle changes conventional quality processes may miss, such as tool wear.
- Industry 4.0 stands for the 4th Industrial Revolution. It is driven by data and advanced technologies, including cyber-physical systems, virtual and augmented reality, the cloud, the Industrial Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. Innovations in industry 4.0 are helping modern manufacturers implement sophisticated automation solutions and smart machines to improve production quality and throughput in their industry 4.0 advanced manufacturing facilities.
- Industrial Internet of Things is the combination of sensors, gauges, instruments and other data collection devices on a production line, connected by an ML/AI-enabled network. It is the driving force behind today’s smart factories. This connectivity facilitates the collection, storage and analysis of massive amounts of data which, using manufacturing analytics software, can be used to identify problems and opportunities on an i4.0 production line.
- Big data refers to the massive volumes of data, usually associated with manufacturing, that is difficult to store and handle using traditional manufacturing data systems. Machine learning has the power to analyze the data and make predictions for the future based on applied input and past experience. Data analytics in manufacturing using a machine learning-powered solution can deliver insights into a plant’s data, helping engineers and quality teams make better decisions.
- Blockchain is a powerful technology that is being leveraged by manufacturers to securely analyze their big data in order to get better insights into their supply chains and track assets with greater precision. This enables them to transform and streamline their data processing operations.
According to a recent Vantage Market Research report, global artificial intelligence in manufacturing is expected to grow by a CAGR of 51.5% over the next six years, reaching a market value of US$17.9 billion by 2028. A Forbes survey on AI found that 44% of respondents from the automotive manufacturing industry classified AI as “highly important” to production, while 49% said it was “absolutely critical to success.” And yet, more than half of the respondents (56%) from the automotive industry said they plan to increase spending in artificial intelligence by approximately 10%.
8 manufacturing applications for AI
1. AI-powered predictive quality analytics
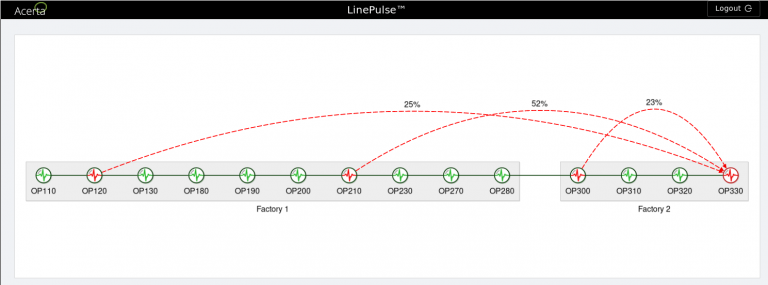
We might as well start with what we know best. The goal of predictive quality analytics is to leverage the data generated before, during, and after the manufacturing production process in order to improve first time through, and reduce scrap and rework.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are used to derive insights from manufacturing data into product quality or predictions about product failures farther down in the production process. Combined with real time alerts, it is now possible to predict when certain quality spills will occur, and provide an opportunity to prevent them. LinePulse provides these capabilities for automotive manufacturers, and displays all relevant manufacturing quality data on a centralized dashboard.
Manufacturers have used the predictive quality analytics of LinePulse for manufacturing to identify faulty transmissions, predict gearbox failures, and detect anomalies in engine misfires. All of these cases involve models based on machine learning — a subset of artificial intelligence — and in each one, the ML/AI models were able to deliver highly accurate results even with minimal training data.
2. Predictive maintenance software

Although predictive quality analytics in manufacturing and predictive maintenance are often lumped into the same category, there are important differences between them. The premise of predictive maintenance is to use data from the production line to anticipate when manufacturing equipment is likely to fail, and then intervene to repair or replace the equipment before that happens.
Nevertheless, as with predictive quality analytics, predictive maintenance depends on being able to synthesize insights from massive data sets, often with minimal training data. Examples of predictive maintenance using AI solutions for manufacturing include machine tool builders forecasting machine spindle issues before they happen, and General Motors using image classification to identify robotic arm failures.
3. Industrial robotics and artificial intelligence solutions for manufacturing
Robots and AI go together like apple pie and ice cream, peanut butter and chocolate, or Wookies and Ewoks: good on their own, but amazing in combination. Although they’ve already been in use for more than half a century, industrial robots have been changing their image in recent decades, from coldly competing against human workers, supplanting them with ruthless efficiency, to friendly helpers that can make line workers’ lives easier rather than stealing their livelihoods. At the center of this shift are collaborative robots, or cobots, which are designed specifically to work with humans.
For example, AI-enabled cobots in the automotive industry can do repetitive, heavy-lifting jobs, like positioning and fastening engine hoods to the body assembly, giving line workers more time to concentrate on jobs that cobots can’t do. Adding AI to cobots enables manufacturers to deploy them faster, monitor production line workspaces for changing conditions and adapt to them.
Regarding industrial robots more generally, AI can improve robot accuracy and reliability as well as enable more advanced forms of mobility. Perhaps most significantly of all, artificial intelligence can play a key role in reducing the programming and engineering effort required to create and implement industrial automation.
4. Computer vision applications of artificial intelligence in manufacturing
Closely tied to industrial robotics, computer vision applications of AI in the industrial space most often involve visual inspections. Computer vision, aided by AI in automotive manufacturing, has two obvious advantages over humans when it comes to visual inspection, namely speed and accuracy. A computer vision system using cameras that are more sensitive than the naked eye and augmented with AI can identify microscopic defects that human inspectors might miss, at a rate they cannot hope to match.
For example, Audi used an AI vision system to identify cracks in the sheet metal from its press shop. Because this solution was based on deep learning — a subtype of machine learning often applied to large, unstructured data sets, such as images — Audi’s engineers spent months training their artificial neural network using several million test images. That initial effort paid for itself however, since the system was able to learn independently from the examples and can now detect cracks in entirely novel images.
5. AI for manufacturing inventory management

Inventory management may not be the most exciting application for AI/ML in manufacturing, but it is a valuable one. According to at least one estimate, inventory amounts to $1.1 trillion in capital. That’s an enormous amount of value that could be unlocked with better inventory management, and artificial intelligence is the key to that. There are myriad ways that AI manufacturing solutions can reduce the costs of maintaining inventory, from optimizing what’s kept on-hand to anticipating gaps before they happen.
Once again, it’s the ability to take in staggering amounts of data and find the patterns hidden within, that make AI solutions for manufacturing such a natural fit. Although it’s not a manufacturer, Amazon is perhaps the largest and best-known example of applying AI to inventory management.
6. Implementing AI solutions for sustainable manufacturing
There are AI solutions for manufacturing that can create more efficient systems to help reduce energy use on the production line. Most sustainability initiatives necessitate the overhauling of the production line, investing in green energy sources, or implementing more efficient technologies – AI manufacturing solutions can deliver production improvements without changes to the manufacturing process.
Computing power and algorithms are becoming more readily available, and data processing and storage costs are dropping, making AI-enabled solutions more common in manufacturing. AI manufacturing solutions are delivering tangible results, such as designing and implementing optimum operating parameters that will reduce energy consumption without adversely affecting production throughput.
For example, Google’s AI-enabled NEST thermostat can efficiently control the heating and cooling of homes and businesses to conserve energy. AI solutions for manufacturing can scale this technology to cover the entire shop floor of large factories, helping manufacturers become more energy efficient.
7. AI to reduce waste in manufacturing
Even if the best practices in manufacturing are followed, human error will always be a factor in the manufacturing process. A defect, or anomaly, on the production line could be missed by the line worker, which could lead to a defective product passing through. Undetected, these minor anomalies can snowball into major faults and wasted materials – impacting negatively on the cost of production for the manufacturer.
AI enabled quality control programs for manufacturing using anomaly detection software can help manufacturers reduce waste, improve product quality, and increase throughput. Most innovative manufacturing companies use AI-enabled anomaly detection solutions to identify manufacturing defects, instead of traditional image-processing methods, as they can pinpoint defects by quickly leveraging large manufacturing datasets.
For example, in the automotive industry, quality control programs for manufacturing that include anomaly detection software can be used to identify faulty door panels and generate an alert when the panel on the production line does not meet predetermined specifications. This enables the engineer and/or line worker to address the problem, thus preventing subsequent door panels from ending up as waste.
8. Supply chain management using machine learning and artificial intelligence
An AI-enabled supply chain management solution can help manufacturers improve their supply chain and logistics operations. Manufacturers are also able to save money through reduced operational redundancies and risk mitigation, and improved supply and demand forecasting, while enhancing their business planning and forecasting capabilities.
A supply chain management solution that incorporates AI can collect and analyze a great deal more inputs and signals than a human is able to process, to deliver accurate and timely decisions faster. The AI-enabled solution is able to adapt to changing conditions in near-real-time and improve its knowledge by processing more data and exposing hidden anomalies in the supply chain better than any human can.
AI in manufacturing: Industry 4.0 and beyond
For most innovative manufacturing companies, the number of applications for artificial intelligence will no doubt continue to increase, as computational resources become less costly. In any case, one thing is certain, it is an exciting time to be working at the intersection of artificial intelligence and the manufacturing industry.
Want to learn more? Get in touch.
Share on social: